
Brix in relation to crop health and quality
Brix in relatie tot gezondheid en kwaliteit van gewassen. De zoete wetenschap van Brix. Brix in relatie tot gezondheid en kwaliteit van gewassen. Brix-waarde verwijst
More yield from better quality
All in just 5 products
25+ years of fertilizer experience
Better and cheaper
Easy to use
PGRs stands for the abbreviation for Plant Growth Regulator. These can be either chemical or natural regulators. However, chemical PGRs are generally referred to when talking about PGRs. Natural PGRs are often referred to as Biostimulants. These are usually extractions that contain natural elements, including natural PGRs. Gen1:11 exclusively uses Biostimulants that contain organic PGRs.
Gen1:11 is 100% free of PGRs
Synthetic or chemical plant growth regulators (PGRs) are substances that can affect plant growth and development. In horticulture, PGRs can be used to achieve specific goals. However, it is important to note that the use of PGRs in growing products for consumption can be a controversial issue and regulations regarding their use may vary by location. In addition, improper use of PGRs can have negative effects on the final product and potentially pose health risks. Well-known PGRs include auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins. Also called plant hormones. Fortunately, the use of (chemical) PGRs is becoming increasingly restricted and their use has already been banned in many places
Biostimulants (with natural pgrs) are not prohibited and improve the overall physiological functions of the plant, promoting health and resilience. They are not fertilizers per se, as they usually do not provide essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus or potassium. Instead, biostimulants work through various mechanisms to improve nutrient use, stress tolerance and overall plant performance.
Biostimulanten vullen meststoffen aan. Het is geen vervanging voor essentiële voedingsstoffen zoals stikstof, fosfor, kalium, calcium, magnesium of fosfor. Kwekers integreren biostimulanten steeds vaker in hun bestaande bemestingsprogramma’s om de efficiëntie van het gebruik van voedingsstoffen te maximaliseren en de algehele gezondheid van planten te bevorderen. Dit is een ontwikkeling die de laatste jaren steeds meer wordt toegepast.
Improved nutrient uptake: Biostimulants can make the uptake of nutrients by plants more efficient, making more effective use of available nutrients from the soil or from fertilizers.
Enhanced root development: Some biostimulants stimulate root growth and branching, improving the plant's ability to explore a larger soil volume in search of nutrients and water.
Stress resistance: Biostimulants can improve a plant's ability to withstand various environmental stresses such as drought, salinity or extreme temperatures. This can be especially beneficial in difficult growing conditions.
Increased crop yield and quality: By optimizing nutrient uptake and improving plant health, biostimulants can contribute to increased crop yields and improved quality of harvested produce.
Stimulated metabolic processes: Biostimulants can activate or enhance certain metabolic processes in plants, leading to increased energy production and more efficient use of resources.
Beneficial microbial activity: Some biostimulants promote the growth and activity of beneficial soil microorganisms, promoting a healthier soil environment for plant growth.
Less environmental impact: The use of biostimulants can contribute to more sustainable and environmentally friendly agricultural practices by reducing reliance on synthetic chemical inputs.
Users of Gen1:11 in their cultivation are unanimously enthusiastic about the quality of the final product. Especially the full aroma of smell and taste stands out among critical users. Some medicinal growers who have used canna and plagron products for decades have now switched to Gen1:11 products

Brix in relatie tot gezondheid en kwaliteit van gewassen. De zoete wetenschap van Brix. Brix in relatie tot gezondheid en kwaliteit van gewassen. Brix-waarde verwijst
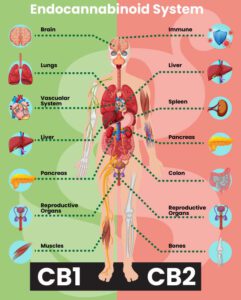
Het endocannabinoïde systeem begrijpen Een korte handleiding voor CB1- en CB2-receptoren Het endocannabinoïde systeem (ECS) speelt een fundamentele rol bij het reguleren van verschillende fysiologische
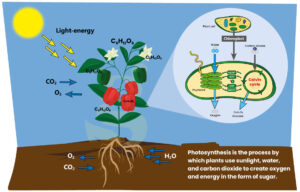
Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae and some bacteria convert light energy into energy in the form of glucose. This process mainly takes place

7 handy tips to prepare for the new garden season Gardening tasks when the spring jitters strike: Spring is a time of renewal and

The development of hydroponic fertilisers through the ages The history of hydroponics is a story of innovation and perseverance, rooted in the quest of the

Creating a successful indoor grow involves more than just light and water. Here are 7 tips to boost your indoor garden.
Brix in relatie tot gezondheid en kwaliteit van gewassen. De zoete wetenschap van Brix. Brix in relatie tot gezondheid en kwaliteit van gewassen. Brix-waarde verwijst
Het endocannabinoïde systeem begrijpen Een korte handleiding voor CB1- en CB2-receptoren Het endocannabinoïde systeem (ECS) speelt een fundamentele rol bij het reguleren van verschillende fysiologische
Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae and some bacteria convert light energy into energy in the form of glucose. This process mainly takes place
7 handy tips to prepare for the new garden season Gardening tasks when the spring jitters strike: Spring is a time of renewal and
The development of hydroponic fertilisers through the ages The history of hydroponics is a story of innovation and perseverance, rooted in the quest of the
Creating a successful indoor grow involves more than just light and water. Here are 7 tips to boost your indoor garden.
Home » 100% PGR Free

Because growing your own is a craft. It takes time, energy, focus, attention, maybe even love. At your own pace, in your own environment. You are the creator.