
Brix in relation to crop health and quality
Brix in relatie tot gezondheid en kwaliteit van gewassen. De zoete wetenschap van Brix. Brix in relatie tot gezondheid en kwaliteit van gewassen. Brix-waarde verwijst
More yield from better quality
All in just 5 products
25+ years of fertilizer experience
Better and cheaper
Easy to use

Growing chili peppers outdoors can be a rewarding experience. Here are some steps to help you successfully grow chili peppers in an outdoor environment.
Choose chili pepper varieties suitable for your climate and the amount of sunlight available at your location. Some popular varieties include jalapeno, habanero, serrano and paprika. When growing chili peppers, choosing the right variety is essential for a successful and satisfying harvest. Here are some factors to consider when choosing the variety of chili peppers
When choosing chili pepper varieties, consider your growing conditions, climate and gardening experience. It is also a good idea to consult local gardening experts or nurseries for recommendations based on your specific region.
Choose a sunny spot. Chili peppers thrive in full sun. Chili peppers need at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight per day for optimal growth and fruit production. Choose a sunny spot in your yard or garden that receives adequate sunlight throughout the day. Although chili peppers thrive in sunlight, they can also be susceptible to scorching or sunburn in extremely hot climates or during heat waves. In intense heat, provide shade or protection during the hottest part of the day, such as with shade cloths or plant them near taller plants that provide partial shade.
If you grow chili peppers outdoors, you have several options for choosing a growing medium. Here are some common choices:
Garden soil: If you have nutrient-rich, well-draining soil in your garden, you can plant chilli directly into the soil. Make sure the soil is loose and well replenished with organic matter for good drainage and nutrient availability.
Raised beds: Creating raised beds gives you more control over growing conditions. Fill the beds with a combination of topsoil, compost and other organic material to create a fertile and well-drained medium.
Container gardening: Growing chilli in container (pots)s is a popular choice for outdoor growing, especially if you have limited space or poor quality soil. Use containers large enough for the root system and make sure they have drainage holes at the bottom.
Whatever medium you choose, it is important to ensure good drainage, aeration and availability of nutrients for the chillies. Check moisture levels regularly and adjust watering accordingly.
Water chilli plants regularly, keeping the soil constantly moist but not drenched. Aim to water once or twice a week, depending on rainfall and temperature. Adjust watering according to weather conditions and the plants' moisture requirements.
Chili peppers benefit from regular fertilisation. Fertilising outdoor-grown chilli can help provide them with the necessary nutrients for healthy growth and abundant fruit production. Here are some guidelines for fertilising chilli in an outdoor environment:
'Slow release' fertilisers - During each growth stage, you can apply a slow-release fertiliser in granular form. Follow the manufacturer's instructions for application rates and mix it into the soil around the plants.
Liquid fertilisers: As chilli plants grow, they will benefit from a balanced fertiliser with a balanced NPK ratio. This provides a good mix of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and potassium (K) to support overall plant health and fruit production. In addition to all the macro elements, a good fertiliser is supplemented with the necessary micro-nutrients
Foliar fertiliser: You can supplement in addition to regular fertilisation by giving foliar feed. Fertilisers are absorbed directly by the leaves and dispensed where needed.
Chili peppers usually ripen gradually. Harvest them when they have reached the desired size and colour. Use secateurs or a sharp knife to cut the chillies from the plant, leaving a short stalk.
Denk eraan uw teeltmethoden aan te passen aan uw specifieke klimaat en de chilipepersoort die u kweekt. Met de juiste zorg, aandacht voor bewatering en bemesting, en bescherming tegen ziekten en plagen, kunt u genieten van een overvloedige oogst van heerlijke chilipepers uit uw tuin.
Have fun growing chilli peppers!

Brix in relatie tot gezondheid en kwaliteit van gewassen. De zoete wetenschap van Brix. Brix in relatie tot gezondheid en kwaliteit van gewassen. Brix-waarde verwijst
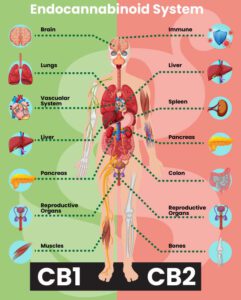
Het endocannabinoïde systeem begrijpen Een korte handleiding voor CB1- en CB2-receptoren Het endocannabinoïde systeem (ECS) speelt een fundamentele rol bij het reguleren van verschillende fysiologische
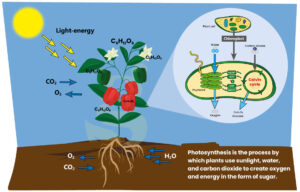
Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae and some bacteria convert light energy into energy in the form of glucose. This process mainly takes place

7 handy tips to prepare for the new garden season Gardening tasks when the spring jitters strike: Spring is a time of renewal and

The development of hydroponic fertilisers through the ages The history of hydroponics is a story of innovation and perseverance, rooted in the quest of the

Creating a successful indoor grow involves more than just light and water. Here are 7 tips to boost your indoor garden.
Brix in relatie tot gezondheid en kwaliteit van gewassen. De zoete wetenschap van Brix. Brix in relatie tot gezondheid en kwaliteit van gewassen. Brix-waarde verwijst
Het endocannabinoïde systeem begrijpen Een korte handleiding voor CB1- en CB2-receptoren Het endocannabinoïde systeem (ECS) speelt een fundamentele rol bij het reguleren van verschillende fysiologische
Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae and some bacteria convert light energy into energy in the form of glucose. This process mainly takes place
7 handy tips to prepare for the new garden season Gardening tasks when the spring jitters strike: Spring is a time of renewal and
The development of hydroponic fertilisers through the ages The history of hydroponics is a story of innovation and perseverance, rooted in the quest of the
Creating a successful indoor grow involves more than just light and water. Here are 7 tips to boost your indoor garden.
Home » Growing chilli peppers

Because growing your own is a craft. It takes time, energy, focus, attention, maybe even love. At your own pace, in your own environment. You are the creator.