
Brix in relation to crop health and quality
Brix in relatie tot gezondheid en kwaliteit van gewassen. De zoete wetenschap van Brix. Brix in relatie tot gezondheid en kwaliteit van gewassen. Brix-waarde verwijst
More yield from better quality
All in just 5 products
25+ years of fertilizer experience
Better and cheaper
Easy to use
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) plays a fundamental role in regulating various physiological processes in the human body. Central to this system are the cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2, which are widely distributed throughout the body. This article provides an overview of CB1 and CB2 receptors, their role and their possible implications for health and well-being.
Imagine a network in your body that helps regulate everything from mood and appetite to pain and immune function. That's the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in a nutshell. It's a fascinating system that scientists are still discovering, but one thing is clear: it plays a vital role in keeping our bodies healthy and balanced. Think of CB1 and CB2 receptors as the messengers of the ECS. CB1 receptors are like the gatekeepers of the brain and nervous system, while CB2 receptors are more like the guardians of the immune system and peripheral tissues.
Imagine a network in your body that helps regulate everything from mood and appetite to pain and immune function. That's the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in a nutshell. It's a fascinating system that scientists are still discovering, but one thing is clear: it plays a vital role in keeping our bodies healthy and balanced. Think of CB1 and CB2 receptors as the messengers of the ECS. CB1 receptors are like the gatekeepers of the brain and nervous system, while CB2 receptors are more like the guardians of the immune system and peripheral tissues.
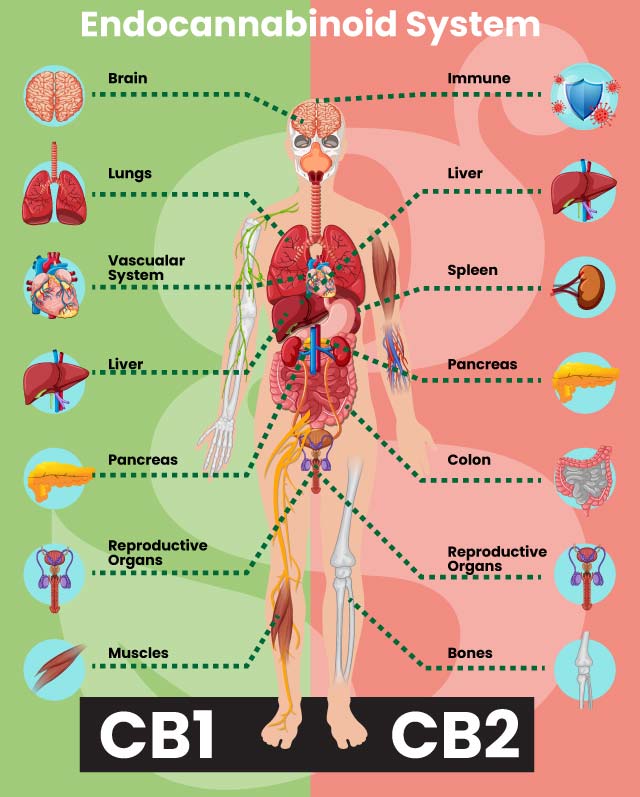
CB1 receptors are mainly located in the brain and spinal cord, where they help regulate things like mood, memory, pain and appetite. CB2 receptors are distributed throughout the body, especially in immune cells, where they help regulate inflammation and immune responses. When CB1 receptors are activated, they can help reduce pain, calm anxiety and stimulate appetite. CB2 receptors, on the other hand, are more concerned with fighting inflammation and supporting immune function. Together, they keep our bodies in balance, or what scientists call homeostasis.
The widespread expression of CB1 and CB2 receptors and their involvement in various physiological processes have led to a growing interest in targeting the ECS for therapeutic purposes. Preclinical and clinical studies have demonstrated the potential of cannabinoids and cannabinoid receptor agonists and antagonists in the treatment of various conditions, including chronic pain, neurodegenerative diseases, inflammatory disorders and psychiatric disorders.
Investigating the endocannabinoid system and cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2 are promising developments for therapeutic intervention in a wide range of diseases and disorders. Further research is needed to elucidate the precise role of CB1 and CB2 receptors in health and disease and to develop safe and effective pharmacological agents that modulate the ECS. Understanding the complexity of the ECS and cannabinoid receptors is essential for harnessing their full therapeutic potential and improving human health.

Brix in relatie tot gezondheid en kwaliteit van gewassen. De zoete wetenschap van Brix. Brix in relatie tot gezondheid en kwaliteit van gewassen. Brix-waarde verwijst
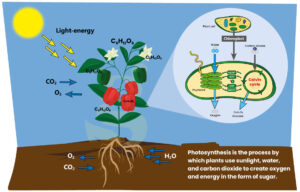
Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae and some bacteria convert light energy into energy in the form of glucose. This process mainly takes place

7 handy tips to prepare for the new garden season Gardening tasks when the spring jitters strike: Spring is a time of renewal and

The development of hydroponic fertilisers through the ages The history of hydroponics is a story of innovation and perseverance, rooted in the quest of the

Creating a successful indoor grow involves more than just light and water. Here are 7 tips to boost your indoor garden.

Transforming urban heat islands into cool and livable cities The power of harnessing greenery for cooler cities As urbanisation increases, cities are struggling over
Brix in relatie tot gezondheid en kwaliteit van gewassen. De zoete wetenschap van Brix. Brix in relatie tot gezondheid en kwaliteit van gewassen. Brix-waarde verwijst
Het endocannabinoïde systeem begrijpen Een korte handleiding voor CB1- en CB2-receptoren Het endocannabinoïde systeem (ECS) speelt een fundamentele rol bij het reguleren van verschillende fysiologische
Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae and some bacteria convert light energy into energy in the form of glucose. This process mainly takes place
7 handy tips to prepare for the new garden season Gardening tasks when the spring jitters strike: Spring is a time of renewal and
The development of hydroponic fertilisers through the ages The history of hydroponics is a story of innovation and perseverance, rooted in the quest of the
Creating a successful indoor grow involves more than just light and water. Here are 7 tips to boost your indoor garden.
Home » The endocannabinoid system and receptors CB1 and CB2

Because growing your own is a craft. It takes time, energy, focus, attention, maybe even love. At your own pace, in your own environment. You are the creator.